Get Certified in Interventional Radiology/Diagnostic Radiology (IR/DR)
Learn the steps to becoming ABR board certified in interventional radiology, including eligibility requirements and the exam process. Visit our alternate pathways page to explore prerequisites, eligibility requirements, and other details for the interventional radiology pathways.
-
Interventional radiologists specialize in image-guided, minimally invasive procedures.
The IR/DR certification process ensures you have the knowledge and skills to provide high-quality patient care. You’ll need to meet specific education, training, and exam requirements to be eligible for certification.
Eligibility Requirements
Integrated IR Requirements
- Complete a year of clinical training
Before starting residency, you must complete a year of clinical training in a program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada (RCPSC) in the U.S. or Canada. To learn more about ACGME clinical year training requirements, refer to Section III.A.2.b).(2).(a) of the ACGME Interventional Radiology Program Requirements.
If you’ve completed accredited training in another specialty, you may be eligible for credit. This is reviewed on an individual basis after the appropriate documentation is submitted to the ABR.
If your clinical year includes a diagnostic radiology (DR) or IR/DR elective:
- It must be in a department with an ACGME-accredited interventional or diagnostic radiology residency program.
- It cannot be longer than two months.
- You can spend no more than three months in radiation oncology and/or pathology.
If you’re in an RCPSC-accredited program, you’ll need a minimum of eight four-week blocks of clinical experiences outside of radiology.
- Complete an accredited residency program
Complete a five-year ACGME-accredited integrated IR residency. It must include:
- Three years of DR training (same as a standard DR residency, which will include some months of IR training) and two years of IR training
- Training in critical care medicine
- Training in periprocedural care and inpatient admitting service
- Pass your exams
- Qualifying (Core) Exam – Taken after 36 months of residency. In limited circumstances, your program director can request permission for you to take the exam earlier. Read the policy for more information.
- Certifying Exams (computer-based and oral components) – After passing the Qualifying (Core) Exam and completing your residency training, you can:
- Take the computer-based component the same calendar year.
- Take the oral component the following calendar year. If you’re already DR certified, you only need to take the oral component.
- Hold a valid state or provincial medical license
If you’re still in training, a valid training license is acceptable.
- Demonstrate ethical standards
The ABR expects all candidates to uphold fundamental moral and ethical principles and exhibit professional behavior throughout the certification process.
Independent IR Requirements
- Complete a DR residency
First, you must complete an ACGME- or RCPSC-accredited DR residency. It may include no more than 16 months in research.
- Complete an independent IR residency
You’ll need to complete a two-year ACGME-accredited independent IR residency, unless you did Early Specialization in IR (ESIR) during your DR residency. If you completed ESIR, you may only need to complete one year of independent IR training if approved by your IR program director.
- Pass your exams
- Qualifying (Core) Exam – Taken after 36 months of residency. In limited circumstances, your program director can request permission for you to take the exam earlier. Read the policy for more information.
- Certifying Exams (computer-based and oral components) – After passing the Qualifying (Core) Exam and completing your residency training, you can:
- Take the computer-based component the same calendar year.
- Take the oral component the following calendar year. If you’re already DR certified, you only need to take the oral component.
- Hold a valid state or provincial medical license
If you’re still in training, a valid training license is acceptable.
- Demonstrate ethical standards
The ABR expects all candidates to uphold fundamental moral and ethical principles and exhibit professional behavior throughout the certification process.
Board Eligibility
Your board eligibility period begins when you complete residency training and lasts for six full calendar years—this is the time allowed by the ABR for you to achieve initial IR/DR certification.
To learn more, read our Board Eligibility Policy.
Residency Requirements and Policies
Residency Completion
Effective July 1, 2026, you must complete your residency within these time limits:
- Integrated Program – Five-year residency within 10 years
- Independent Program – Two-year residency within four years
Taking Leave
Personal and family needs are important during residency. We support you in taking leave when you need it.
To learn more, read our Residency Leave Policy.
-
Apply for Certification
Once you begin your residency, your program director or coordinator will submit your name and email address to the ABR, so we’ll know you have officially started training.
As soon as we receive your information, we’ll send a welcome notification with instructions on how to log in to myABR and start your application. You’ll need:
- Medical school information
- Internship certificate (PDF copy)
- Residency start date
- Residency training dates by year
- ABNM certification, if applicable
You can submit your application between July 1 and October 31. The application fee is due when you apply. Applications are reviewed in the order they’re received.
-
Exam Process
Certification exams assess your knowledge, skills, and readiness for independent practice. The IR/DR certification process includes two exams:
- Qualifying (Core)
- Certifying (this exam includes both a written and oral component)
Qualifying (Core) Exam
This computer-based exam assesses your fundamental knowledge and clinical judgment across all key diagnostic radiology and integrated interventional radiology/diagnostic radiology areas. This includes anatomy, pathophysiology, diagnostic imaging, interventional procedures, and physics.
Exam Content
This exam covers a broad range of practice domains, including:
- Breast imaging
- Cardiovascular imaging
- Computed tomography
- Gastrointestinal imaging
- Genitourinary imaging
- Interventional radiology
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Musculoskeletal radiology
- Neuroradiology
- Noninterpretive skills
- Nuclear radiology
- Pediatric radiology
- Physics
- Radiography/fluoroscopy
- Thoracic radiology
- Ultrasound
- Radioisotope Safety Content
Exam Format, Timing, and Scoring
Format
This computer-based exam is administered remotely over three days and takes approximately five and a half hours per day. Explore exam formats in more depth, including a breakdown of how many questions are in each section, in the Qualifying (Core) Exam Guide.
Timing
The ABR offers the Qualifying (Core) Exam twice a year (typically in late May or early June and November).
Physics Integration
There’s no separate physics exam; physics questions are embedded throughout the exam. These questions reflect the fundamental medical physics commonly encountered by radiologists in interpreting images, executing procedures, and consulting with colleagues and staff.
Performance on physics-related questions is factored into the overall score.
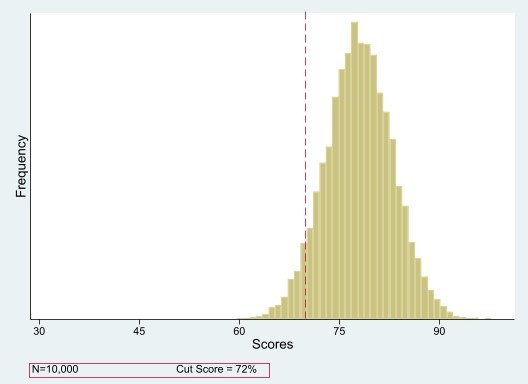
Scoring
The Qualifying (Core) Exam is scored using a criterion-referenced scoring method. Your score is based on how well you do compared with a fixed standard — not how everyone else does.
The Qualifying (Core) exam is scored as a whole, and the result is either pass or fail.
- All categories must be passed together.
- If you don’t meet the standard, you must retake the entire exam.
Learn more about exam scoring.
Certifying Exam
The Certifying Exam tests your ability to interpret information, develop differential diagnoses, and manage patient care.
Exam Content
The exam consists of two components:
- Computer-based Component
- Includes Essentials of Diagnostic Radiology and one fundamental interventional radiology module. The Essentials module includes Noninterpretive Skills (NIS) topics that are important in radiology practice, like contrast reaction management, error prevention, communication, professionalism, and ethics.
- Oral Component
- Includes four 30-minute oral exams covering the full scope of interventional radiology, including image interpretation, image-guided procedures, and periprocedural management, and guided case discussions.
- Is conducted one-on-one with four different examiners.
Beginning in 2029, the IR/DR Certifying Exam process will include two oral exams: the Diagnostic Radiology (DR) Oral Exam and the Interventional Radiology (IR) Oral Exam. You’ll need to pass both to complete the certification process.
Please note that the computer-based portion of the current IR/DR Certifying Exam will no longer be offered after 2028.
Exam Format, Timing, and Scoring
Format
The IR/DR Certifying Exam is conducted remotely and formatted as follows:
- Computer-based exam that takes approximately 4 hours.
- Separately administered oral exam that takes approximately 3 hours.
Explore exam formats in more depth, including a breakdown of how many questions are in each section, in the Oral Certifying Exam Guide and Computer-based Certifying Exam Guide.
Timing
The exam components are held on separate days. You can take the computer-based component in the calendar year you complete training and the oral component in the calendar year after you complete training.
You don’t need to pass the computer-based component before you take the oral component; however, you will need to pass both to achieve IR/DR certification.
If you’re already certified in DR, you don’t have to take the computer-based component.
Upcoming computer-based component and oral component certifying exam dates.
Scoring
The certifying exams are scored using a criterion-referenced scoring method. Your score is based on how well you do compared with a fixed standard — not how everyone else does.
Each IR Certifying Exam component is scored as a whole, and the result is either pass or fail.
- All categories or modules on each component must be passed together.
- If you don’t meet the standard, you must retake the entire exam component.
- The computer-based and oral components are scored separately. You must pass both parts to pass overall. You can retake them separately if you only fail one.
Learn more about exam scoring.
-
Exam Registration
Once you’re eligible to take an exam, the ABR will send an email invitation three to four months before your exam with instructions on completing registration in myABR.
To ensure you receive these emails, update your contact information, add @theabr.org to your approved senders list, and keep an eye on your spam folder.
Before registering for an exam, you’ll need to pay all exam fees.
-
Exam Preparation
Experienced volunteers from all practice settings create ABR exams. We offer study guides and exam blueprints to help you prepare, but you’ll need to find the study materials that work for you. Keep in mind that materials from other organizations won’t always match the format, scope, or difficulty of ABR exams.
To learn more about how exams are created and scored, please see:
- Information for volunteers – how volunteers create exam questions
- Illustrated life cycle of an ABR exam item– a look at the extensive QA process that each question goes through
- Exam scoring and results – how we evaluate your exam
Studying for IR/DR Exams
Preparation for the IR/DR exams involves understanding the breakdown of the material across the various practice domains.
The Qualifying (Core) Exam contains:
- Critical Concepts – The must-know knowledge and skills for your training level.
- Domain Blueprint – A breakdown of subspecialty topics and their percentage distribution on the exam.
- Domain Overview – A detailed reference of potential exam material (not a study guide, but great for understanding the scope of material that might be on the exam).
In addition to studying the relevant practice domains, you’ll need to know the content in the Noninterpretive Skills (NIS), Physics, and Radioisotope Safety Content (RISC) study guides.
The Certifying Exam computer-based component contains:
- Two Required Modules – The essentials of diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology. The diagnostic radiology module includes noninterpretive skills.
The second portion of the RISC is also integrated into the computer-based component of the Certifying Exam. For studying, please refer to the RISC Domain Document and Radioisotope Safety Content (RISC) Study Guide.
The Certifying Exam oral component contains:
- Four categories – While some cases within a category may focus more heavily on a specific area, you’ll always be assessed on your skills in image-guided procedures, periprocedural patient management, and image interpretation. Your examiners will evaluate all three competencies throughout the exam.
To help you prepare, we’ve created an oral exam reenactment that shows how cases are presented and scored.
Study Tools and Resources
Qualifying (Core) Exam:
Certifying Exam:
- Essentials of Diagnostic Radiology Study Guide
- IR/DR Certifying Exam – Computer-based Component Study Guide – for IR candidates who are not certified in DR and are completing the computer-based exam.
- IR Oral Exam Study Guide
- IR Oral Exam Reenactment Video
- Oral Certifying Exam Guide
- Computer-based Certifying Exam Guide
General:
You’ll also need to know content from the following guides for the qualifying and certifying exams.
- Physics Study Guide
- Radioisotope Safety Content (RISC) Study Guide
- Noninterpretive Skills Study Guide
Please note, for the 2025 Noninterpretive Skills Guide, we’ve updated page 35, changing “5 gauss line” to “9 gauss line” to match current standards.
Exam Readiness Checks
After you’re registered for an upcoming computer-based exam, you’ll receive a link to the Exam Readiness Check. You can also access it by logging in to myABR.
This quick check helps you get comfortable with the exam interface, navigation, and tools before your exam day.
Here’s how it works:
- Do the readiness check exactly like you’ll take the exam – on the same computer and in the same location.
- Once you’ve launched the readiness check, a quick technical verification will check your camera, microphone, internet, and software. Learn more about technical requirements for remote exams.
- You’ll be required to complete an identification check by scanning your ID and taking a selfie.
If you change computers or locations before exam day, we recommend repeating the check to ensure everything works as expected.
Sample Questions
Once you complete the Exam Readiness Check, you’ll get access to a set of sample questions. They’ll help you get familiar with the different question formats you can expect on the exam, such as:
- Multiple-choice – Most questions follow this format.
- Drag and drop – You’ll have to identify an anatomical site by clicking on the correct spot in an image.
While taking your exam, you can flag items within sections to go back to if you have time. Once you leave a section, you cannot return to it.
Answer Sheets for Sample Questions
- IR/DR Qualifying (Core) Exam Sample Questions Answer Sheet
- IR/DR Certifying Exam Sample Questions Answer Sheet
-
Current Scoring Status
Exam results will be available in myABR about one month after your exam. You’ll receive an email notification as soon as your results are posted.
Results for the Qualifying (Core) Exam are in the following phase of the scoring process. This graphic will change as the process progresses. Check back regularly after your exam for real-time updates.

Learn more about ABR exam scoring and results.
-
History of Aggregate Exam Results
To help you understand the typical performance of first-time takers on IR/DR exams, we’ve compiled tables showing the pass rates from recent Qualifying (Core) and Certifying exams.
Qualifying (Core) Exam
Exam ID Percent Passed1 Total Examinees 2016 91 1281 2017 94 1283 2018 86 1287 2019 84 1337 2021 Feb 89 1392 2021 June 89 1486 2022 94 1477 2023 95 1458 2024 94 1445 2025 91 1485 1First-time takers (Residents ONLY)
Certifying Oral Exam
First-Time Takers
Year Percentage Passed Total First-Time Takers 2017 94 263 2018 90 319 2019 89 340 2021 90 603 2022 87 299 2023 88 291 2024 89 215 2025 88 190