Diagnostic Content Guide and Sample Questions
Last verified on April 25, 2025
On this page
PLEASE NOTE: List of Constants and Physical Values for Use on the Part 2 Physics Exams
The ABR provides candidates with a list of constants, physical values, and related information, which can be found on this page. While the list includes many constants and physical values, the ABR does not warrant the list as a compilation of all constants and physical values needed on the examinations. Candidates should review the list carefully before their examinations to familiarize themselves with the contents and list organization. Please note that although constants are provided, equations are not typically provided.
Content Guide
The content of all ABR exams is determined by a panel of experts who select the items based on a content guide that the ABR publishes. The content guides are assembled using guidance from medical physics organizations. The content guides are general documents, and individual exam items may not appear to be exactly congruent with the content listed in the guide. In addition, since there is only a limited number of items on any exam, selected items will only be a sample from the larger domain of the content guide. To understand how exam questions are written and learn more about different types of exam questions, please see the ABR Item Writers’ Guide. For a look at the extensive QA process that each question goes through, please see the Illustrated Life Cycle of an ABR Exam Item. For information about the remote exam delivery format and what to expect on exam day, please see the Medical Physics Remote Qualifying Part 2 Exam Guide.- Radiography, Mammography and Fluoroscopy
- Design and fundamentals of operation
- Acquisition parameters and routine clinical procedures
- Patient dose calculations
- Specialized systems
- Clinical medical physics practice
- Image quality
- Computed Tomography
-
- Design and fundamentals of operation
-
- Acquisition parameters and routine clinical procedures
-
- Patient dose calculations
- Specialized CT systems
- Clinical medical physics practice
-
- CT image quality
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
-
- Design and fundamentals of operation of MRI systems
-
- Acquisition parameters and routine clinical procedures
- Safety considerations
- Clinical medical physics practice
- MRI image quality
- Ultrasound
-
- Design and fundamentals of operation of ultrasound systems
- Acquisition parameters and routine clinical procedures
- Biological risks
- Specialized ultrasound systems
- Clinical medical physics practice
- Ultrasound image quality
- Imaging informatics, Display and Processing
-
- Imaging informatics standards
-
- Workstations and reading environments
-
- Image processing and quality metrics
- Radiation Biology, Dosimetry and Institutional Safety
-
- Biological Effects of Radiation
-
- Dosimetry Fundamentals
-
- Radiation Protection
- Pregnant patient management
- Room Shielding Design
- Professionalism and Ethics
- Guidelines and code of conduct
Sample Questions
Simple Questions
(includes new item types)-
- For a radiograph acquired with automatic exposure control, an increase in which of the following factors will increase patient skin dose?
-
- Tube current (mA)
- Tube voltage (kV)
- Patient thickness
- Focal spot size
- Source-to-image distance
-
- A region of interest (ROI) in a CT image has an intensity of -30 HU. What is the ratio of the linear attenuation coefficient for the ROI to that of water?
-
- 0.70
- 0.97
- 1.00
- 1.03
- 1.30
-
- As a potential contrast agent for ultrasound, which of the following materials is expected to be the strongest scatterer for a fixed concentration of small (< 5 μm) particles?
-
- Encapsulated polymer
- Encapsulated lipid
- Encapsulated gas
- Encapsulated iodine
-
- Which one of the following objects will have the highest MR signal in a brain image acquired with a spin echo pulse sequence of TR=2500 ms and TE=100 ms?
-
- Gray matter
- White matter
- Lens of the eye
- Cerebrospinal fluid
-
- According to NCRP Report No. 116, what is the annual occupational equivalent dose limit for an extremity?
-
- 0.5 Sv
- 1.5 Sv
- 5 Sv
- 15 Sv
- 50 Sv
-
- For a radiograph acquired with automatic exposure control, an increase in which of the following factors will increase patient skin dose?
Answers for this section:
1. C
2. B
3. C
4. D
5. A
New Item Types
Fill-in-the-blank
The candidate must type in the correct response:
-
- According to MQSA regulations, the calculated average glandular dose to the ACR phantom for a single craniocaudal view must be less than ___________ mGy.
Answer = 3
Point-and-click
-
- Point and click on the x-ray tube.
Answer: Clicking any place inside the yellow box is correct.
R-Type
Lead-in:
The following is a list of components of an image intensifier fluoroscopy system. The system has three magnification modes: 23 cm, 15 cm, and 12 cm. Identify the component that is the best answer for each question. Each option may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
-
- Which major component of an image intensifier system has the smallest physical size?
- Input phosphor
- Photo cathode
- Focusing electrodes
- Magnetic shielding
- Output phosphor
- Charge-coupled device array (2k × 2k)
- Flat panel monitor (1k × 1k)
- Which major component of an image intensifier system has the smallest physical size?
-
- Which component is held at the most negative electric potential?
- Input phosphor
- Photo cathode
- Focusing electrodes
- Magnetic shielding
- Output phosphor
- Charge-coupled device array (2k × 2k)
- Flat panel monitor (1k × 1k)
- Which component is held at the most negative electric potential?
-
- Which component is used to minimize S-distortion?
- Input phosphor
- Photo cathode
- Focusing electrodes
- Magnetic shielding
- Output phosphor
- Charge-coupled device array (2k x 2k)
- Flat-panel monitor (1k x 1k)
- Which component is used to minimize S-distortion?
- Which component determines the limiting spatial resolution in normal (23 cm) mode?
- Input phosphor
- Photo cathode
- Focusing electrodes
- Magnetic shielding
- Output phosphor
- Charge-coupled device array (2k × 2k)
- Flat panel monitor (1k × 1k)
Answers:
1. F
2. B
3. D
4. G
Case-based Items
NOTE: The candidate will not be able to return to the previous question to change his or her answer:
-
- A 15-mm-thick slice is imaged using a conventional spin-echo pulse sequence with a TE of 100 ms and a TR of 2500 ms. How long after the excitation pulse is the 180 degree refocusing pulse applied?
- 50 ms
- 100 ms
- 500 ms
- 1000 ms
- 1250 ms
- A 15-mm-thick slice is imaged using a conventional spin-echo pulse sequence with a TE of 100 ms and a TR of 2500 ms. How long after the excitation pulse is the 180 degree refocusing pulse applied?
BLOCK: After you move to the next question, you will be unable to go back to change your answer.
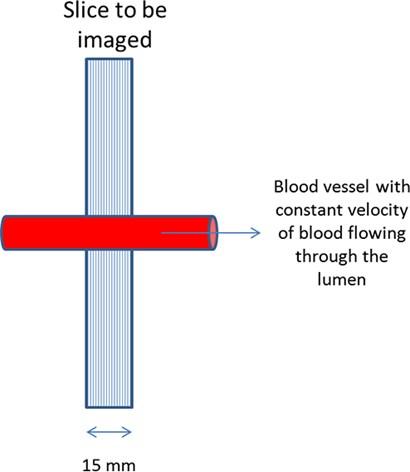
- A 15-mm-thick slice is imaged using a conventional spin-echo pulse sequence. The refocusing pulse is applied at 50 ms after the excitation pulse. What is the minimum velocity of the blood in the lumen of the vessel so that a flow void is observed on the corresponding image?
- 100 mm/s
- 300 mm/s
- 500 mm/s
- 700 mm/s
Answers:
1. A
2. B